Установим haproxy для предотвращения небольших DoS атак
Подключаем репозиторий EPEL
# wget http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/5/i386/epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm # rpm -Uvh epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm
Либо
# rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/5/i386/epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm
Устанавливаем haproxy
# yum -y install haproxy
Добавляем в автозагрузку
# chkconfig haproxy on
Результат
# chkconfig --list | grep haproxy haproxy 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
Скачиваем конфигурацию antidos.cfg
Переименуем файл в папке /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
We assume that the web server has been moved to port 8080 on the loopback, and that haproxy is running on port 80. Note that Apache will have to be configured to get the client’s IP address from the X-Forwarded-For header (mod_rpaf can do that).
Устанавливаем apache на 8080 порту:
# cat /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf | grep Listen # Listen: Allows you to bind Apache to specific IP addresses and/or # Change this to Listen on specific IP addresses as shown below to Listen *:8080
Устанавливаем mod_rpaf , как мы делали ранее
# rpm -ihv http://centos.alt.ru/repository/centos/5/x86_64/centalt-release-5-3.noarch.rpm # yum -y –enablerepo=CentALT install mod_rpaf
Прописываем в /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
LoadModule rpaf_module modules/mod_rpaf-2.0.so RPAFenable On RPAFsethostname Off RPAFproxy_ips 127.0.0.1 RPAFheader X-Real-IP
Перезагружаем apache
# service httpd restart Stopping httpd: [ OK ] Starting httpd: [ OK ]
Перезагружаем Haproxy
# service haproxy restart Stopping haproxy: [ OK ] Starting haproxy: [ OK ]
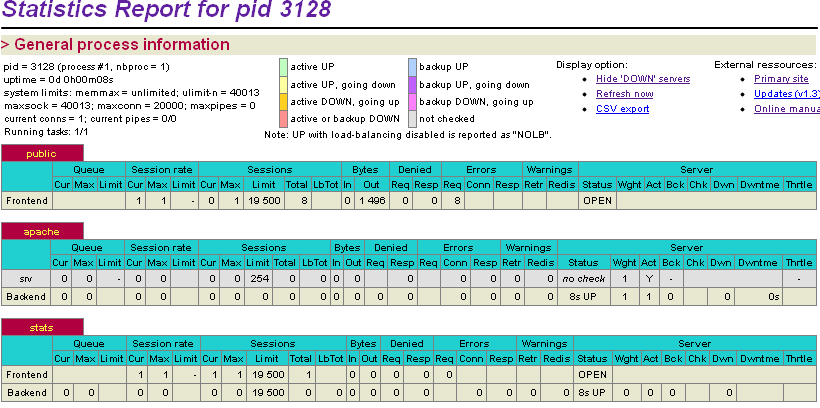
Статистика Haproxy
Enable the stats page on a dedicated port (8888). Monitoring request errors on the frontend will tell us how many potential attacks were blocked.